REST API
Published by
sanya sanya
REST stands for Representational State Transfer. It is an architectural style for designing networked applications. It defines a set of principles and constraints for building web services.
Express.js is a popular web application framework for Node.js that makes it easy to build web servers and APIs.
When we talk about a REST API in Express.js, we're referring to using the Express.js framework to create an API that adheres to the principles of REST. This means designing the API to be stateless, using HTTP methods for different operations, and following the principles of resource identification, representation, and manipulation.
"Stateless" refers to the property of the API where each client request to the server must contain all the information necessary to understand and process the request, without the server relying on any previous communication or session context.
Some key concepts related to building a REST API in Express.js.
HTTP Methods
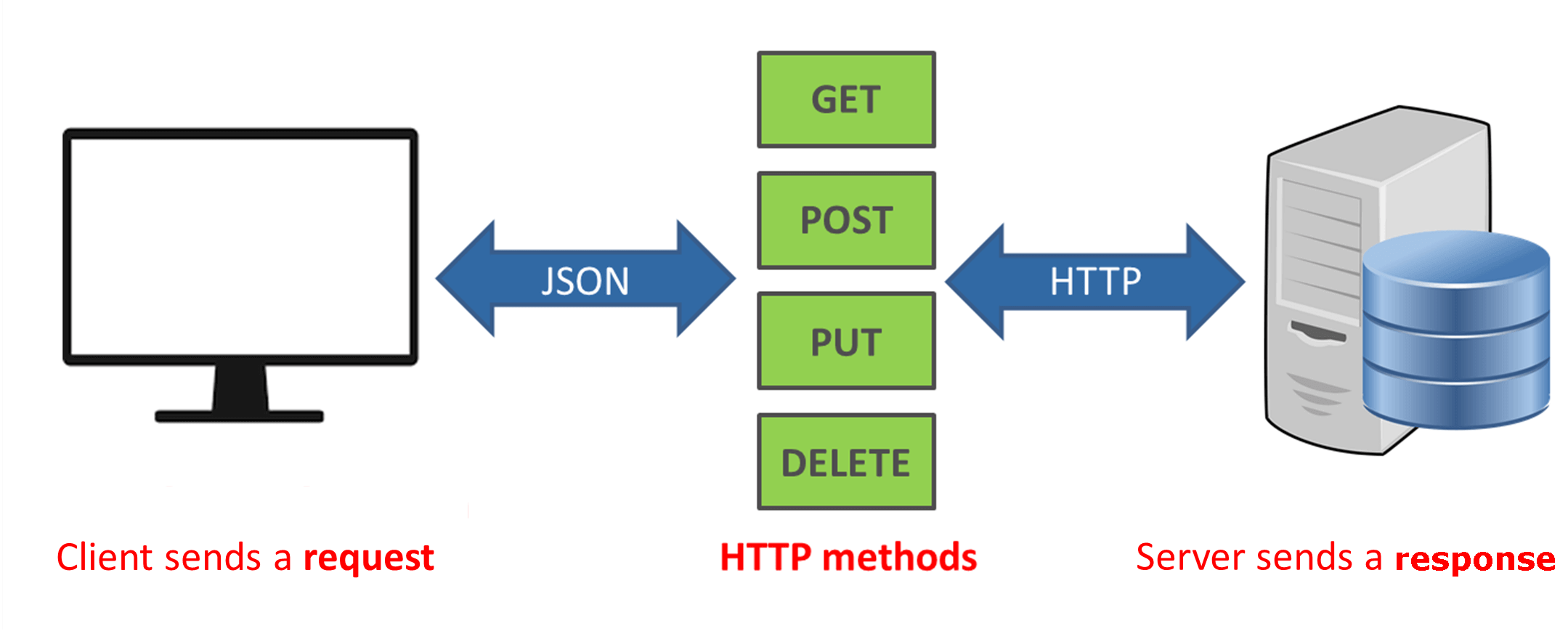
The RESTful APIs use HTTP methods (verbs) to perform different actions on resources. The commonly used methods are -
- GET- This method is used to retrieve a resource or a collection of resources.
- POST - Create a new resource.
- PUT - Update an existing resource.
- DELETE - Remove a resource.
Routes and Endpoints
In Express.js, you define routes and endpoints to handle specific requests. A route specifies a URL pattern, and an endpoint is a combination of a route and an HTTP method.
For example, you can have an endpoint for retrieving users at the /api/users route with the GET method.
Request and Response
Express.js provides request and response objects that contain information about the incoming request and allow you to send the response back to the client.
You can access parameters, query strings, headers, and request bodies from the request object, and send data, headers, and status codes in the response object.
Middleware
Express.js middleware functions allow you to add additional functionality to your API.
You can use middleware to handle common tasks like parsing request bodies, validating input, authenticating users, and handling errors.
Data Storage
REST APIs often interact with a database or another data source to store and retrieve data.
Express.js allows you to use various databases and ORMs (Object-Relational Mappers) such as MongoDB, PostgreSQL, or Sequelize to interact with the data.
Library
WEB DEVELOPMENT
Basic
Frontend
Backend
Node JS
Node Modules
Restful Routing
Static Files
REST API
Introduction to Node JS
GET vs POST
Database
Interview Questions
FAANG QUESTIONS
On this page
HTTP Methods
Routes and Endpoints
Request and Response
Middleware
Data Storage

