Linked List Cycle
Published by
sanya sanya
Detect a cycle-

Using Floyd’s Cycle-Finding method- This algorithm is used to find a cycle/loop in a linked list. Two pointers, slow and fast are used in this algorithm.
Algorithm:
- Traverse the linked list using 2 pointers
- Move the slow pointer by 1 and fast by 2
- If these pointers meet at any point, this means that cycle is present. If pointers do not coincide, cycle is not present.
Code:
bool detectLoop (node* head){
node*slow=head;
node*fast=head;
while(fast!=NULL && fast->next!=NULL){
slow=slow->next;
fast=fast->next->next;
if(slow==fast){
return true;
break;
}
}
return false;
}
Using single pass- To detect a cycle in a linked list using a single pass algorithm, concept of “hash set” or “visited set” can be used. While traversing the list, keep adding visited nodes in the set. If you encounter a node that is already in the set, it means there is a cycle.
Algorithm:
- Initialize an empty hash set or visited set
- Traverse the list starting from head
- For each node in the list,
- If the current node is already present in set, cycle is detected. Return true
- Otherwise, add the current node to the set.
- If the traversal reaches end of list without finding cycle, return false.
Code:
bool detectCycle(node* head){
if(head==NULL){
return false;
}
unordered_set<node*>visitedSet;
node*current=head;
while(current!=NULL){
//If the current node is already in the set, cycle is detected
if(visitedSet.find(current)!= visitedSet.end())
return true;
//Add current node to set
visitedSet.insert(current);
//Move to the next node
current=current->next;
}
//No cycle detected
return false;
}
Find size and length of cycle-
Using Floyd’s method:
Algorithm:
- Find common point of cycle using Floyd’s cycle detection algorithm.
- Store this common point in a pointer and initialize count to 0.
- Traverse the list until same node is reached again and increment count while traversing.
- Print count when node is reached.
Code:
int lengthCycle(node* n){
int count=1;
node* temp=n;
while(temp->next!=n){
count++;
temp=temp->next;
}
return count;
}
int detectLoop (node* head){
node*slow=head;
node*fast=head;
while(fast!=NULL && fast->next!=NULL){
slow=slow->next;
fast=fast->next->next;
if(slow==fast){
return lengthCycle(slow);
}
}
//If no loop is detected
return 0;
}
Using single pass:
Algorithm:
- Find the node which is already present in the visitedSet.
- Store this node in a pointer and pass in length function.
- Initialize count to 0.
- Traverse the list until same node is reached again and increment count while traversing.
- Print count when node is reached.
Code:
int lengthCycle(node* n){
int count=1;
node* temp=n;
while(temp->next!=n){
count++;
temp=temp->next;
}
return count;
}
int detectCycle(node* head){
if(head==NULL){
return 0;
}
unordered_set<node*>visitedSet;
node*current=head;
while(current!=NULL){
//If the current node is already in the set, cycle is detected
if(visitedSet.find(current)!= visitedSet.end()){
return lengthCycle(current);
}
//Add current node to set
visitedSet.insert(current);
//Move to the next node
current=current->next;
}
//No cycle detected
return 0;
}
Remove cycle: If a cycle is detected, removing that cycle might be needed. This can be achieved in the following ways.
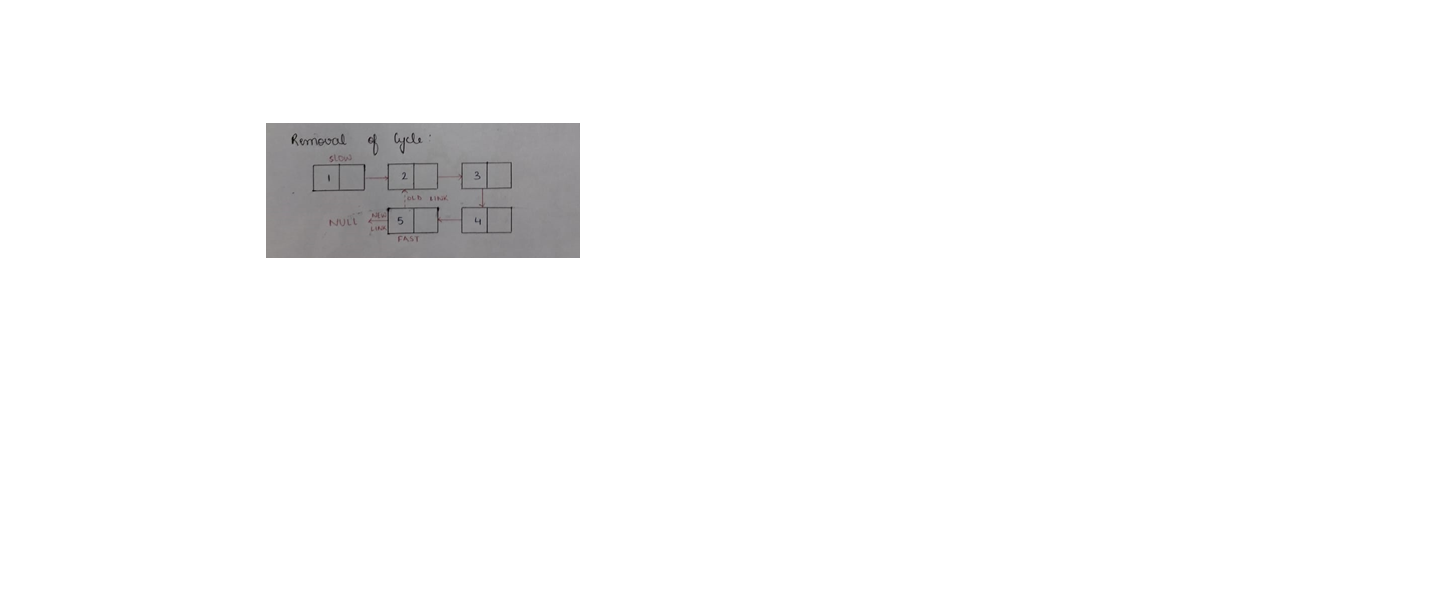
Using Floyd’s Cycle Finding Algorithm:
Algorithm:
- If the cycle is detected using Floyd’s detection method, move the slow pointer to head.
- Move both slow and fast pointer by 1.
- When fast->next==slow, that is the end of the loop
- Point fast to NULL in order to break the loop
Code:
** void detectLoop (node* head){
if (head==NULL || head->next ==NULL)
return;
node*slow=head;
node*fast=head;
while(fast!=NULL && fast->next!=NULL){
slow=slow->next;
fast=fast->next->next;
if(slow==fast){
break;
}
}
if(slow==fast){
slow=head;
if (slow==fast){
while(fast->next!=slow)
fast=fast->next;
}
else{
while(slow->next!=fast->next){
slow=slow->next;
fast=fast->next;
}
}
fast->next=NULL;
}
}
Using single pass: Method of hashing can be used for the single pass algorithm as follows.
Algorithm:
- Hash the addresses of the linked list nodes in an unordered map
- Iterate over the list and check if element already exists
- If it is already present in the map, and is the first node of cycle
- Hence, point the previous node to NULL to break the cycle
Code:
void removeCycle(node* head){
unordered_map<node*,int>visited;
//Create a pointer
node* last =NULL;
while(head!=NULL){
//If node does not exist already, insert it
if(visited.find(head) == visited.end()){
visited[head]++;
last=head;
head=head->next;
}
//If present, cycle exists so make the last node’s next as NULL
else{
last->next=NULL;
break;
}
}
}
Library
WEB DEVELOPMENT
FAANG QUESTIONS

