Glossary of Graphs
Published by
sanya sanya
Types of Graphs:
The graphs can be divided into two categories namely Weighted and Unweighted Graph:
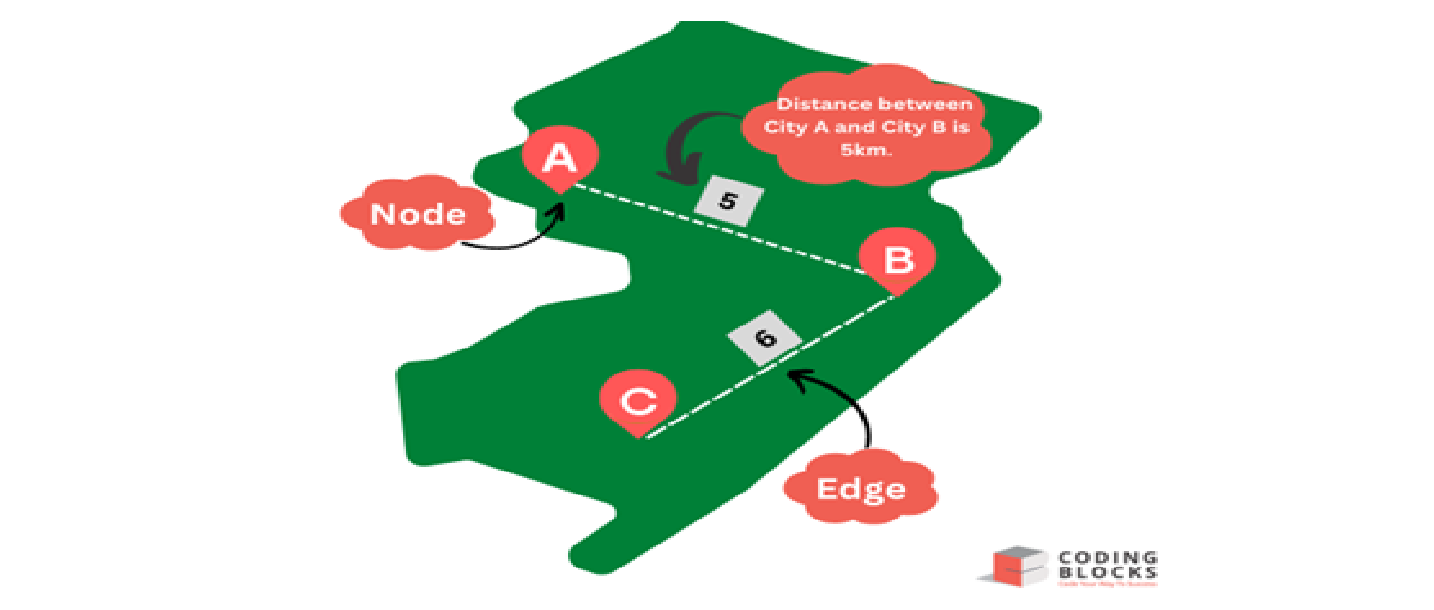
- Weighted Graph: A graph data structure called a "weighted graph" has weights assigned to each edge. Any other metric pertinent to the relationship between the nodes may be used as the weight instead of distance.
For Example, in a road network connecting two cities the weight of edge can be used to determine the distance between the two cities.
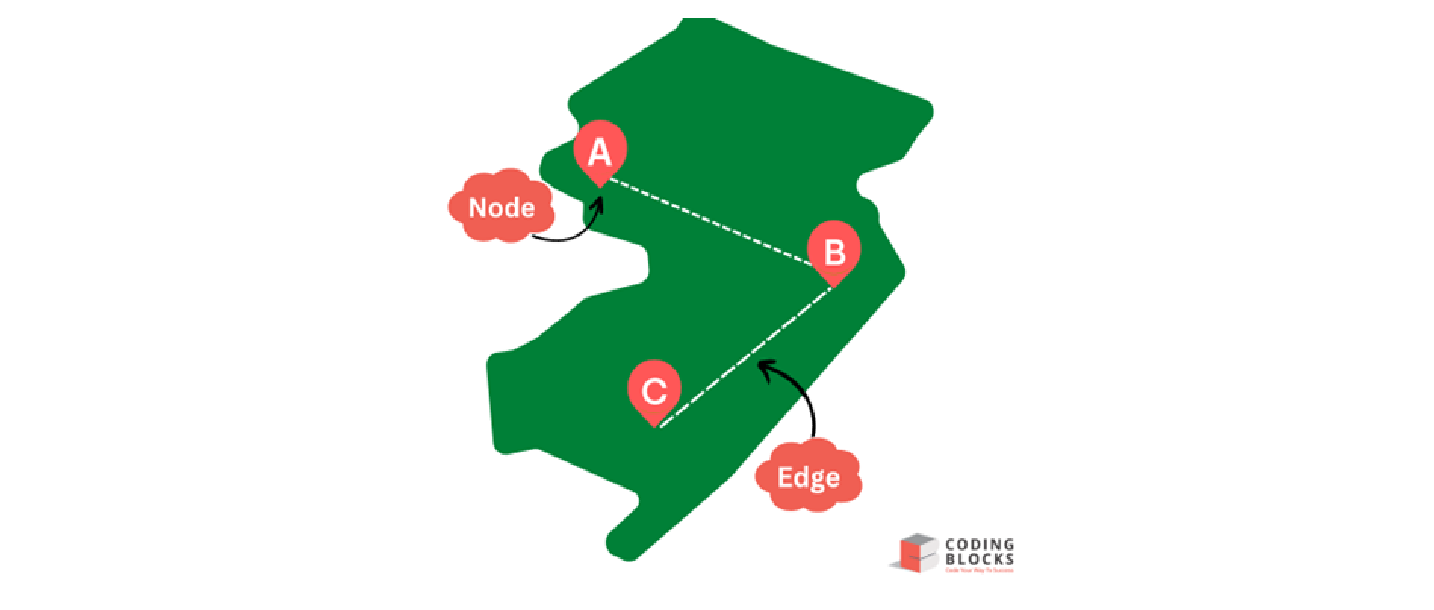
- Unweighted Graph: A graph data structure called an unweighted graph has edges without a weight assigned to them. The edges in this kind of graph merely denote a link or relationship between two nodes.
- Vertices:
A vertex is a basic component of a graph to which edges are joined. Vertex is another name for a node. It serves to represent an entity or object in a graph and to represent the connections between objects.
- Edges:
A connection between two vertices (or nodes) in a graph is represented by an edge. While edges in unweighted networks simply signify a connection between two vertices, in weighted graphs they are given a weight.
Types of Edges:
Edges can be classified into two groups namely Directed Edge and Un-Directed Edge.
- Directed Edge:
A directed edge, also known as an arc, is a one-way connection between two vertices in a directed graph.
It has a direction, starting from the first vertex (also known as the tail) and ending at the second vertex (also known as the head).
For example, in a social network, a directed edge from node A to node B can represent A following B, but not vice versa.
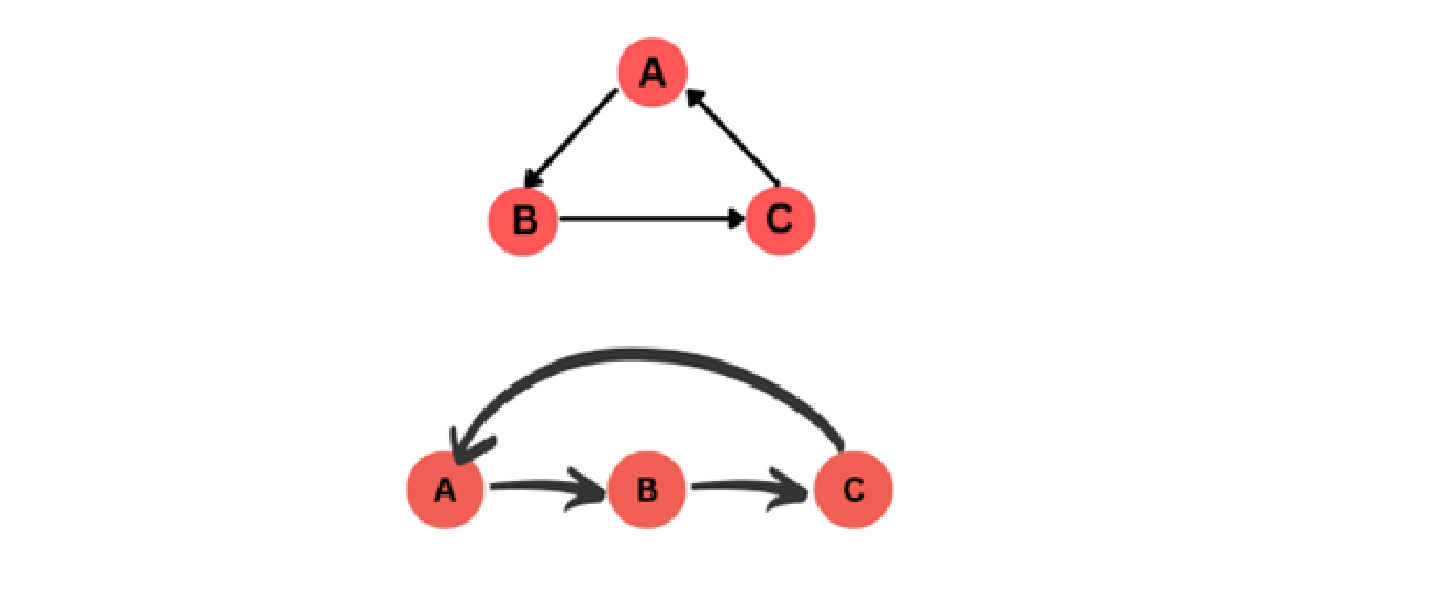
- Un-directed Edge:
An undirected edge is a two-way connection between two vertices in an undirected graph. It does not have a specific direction and represents a symmetrical relationship between the vertices.
For example, in a social network, an undirected edge between node A and node B can represent a mutual friendship between A and B.

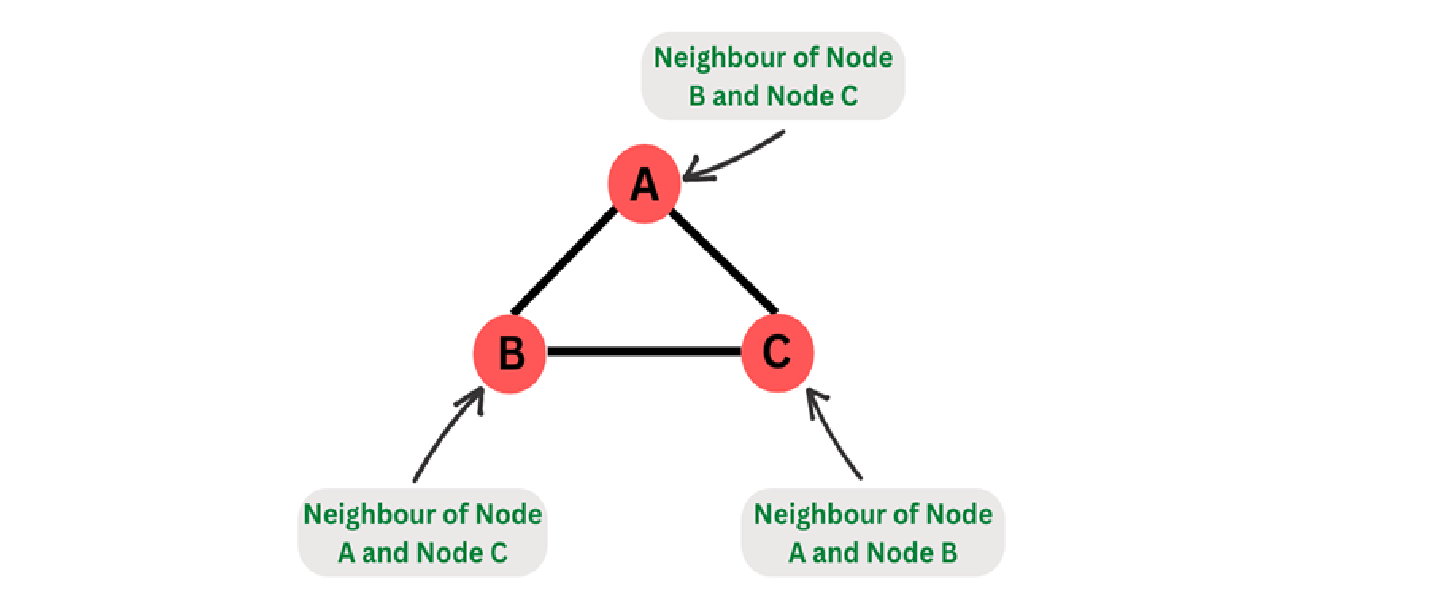
Neighbors of a Node:
"Neighbours of a node" refers to the nodes that are directly connected to a specific node in a graph structure.
Directed Graph:
-
A type of graph structure known as a directed graph has edges that are directed from one vertex (node) to another. A directed graph comprises ordered pairs of vertices called edges, each of which has a source node and a target node.
-
Directed graphs are used to model many real-world situations, such as relationships between individuals in Instagram.
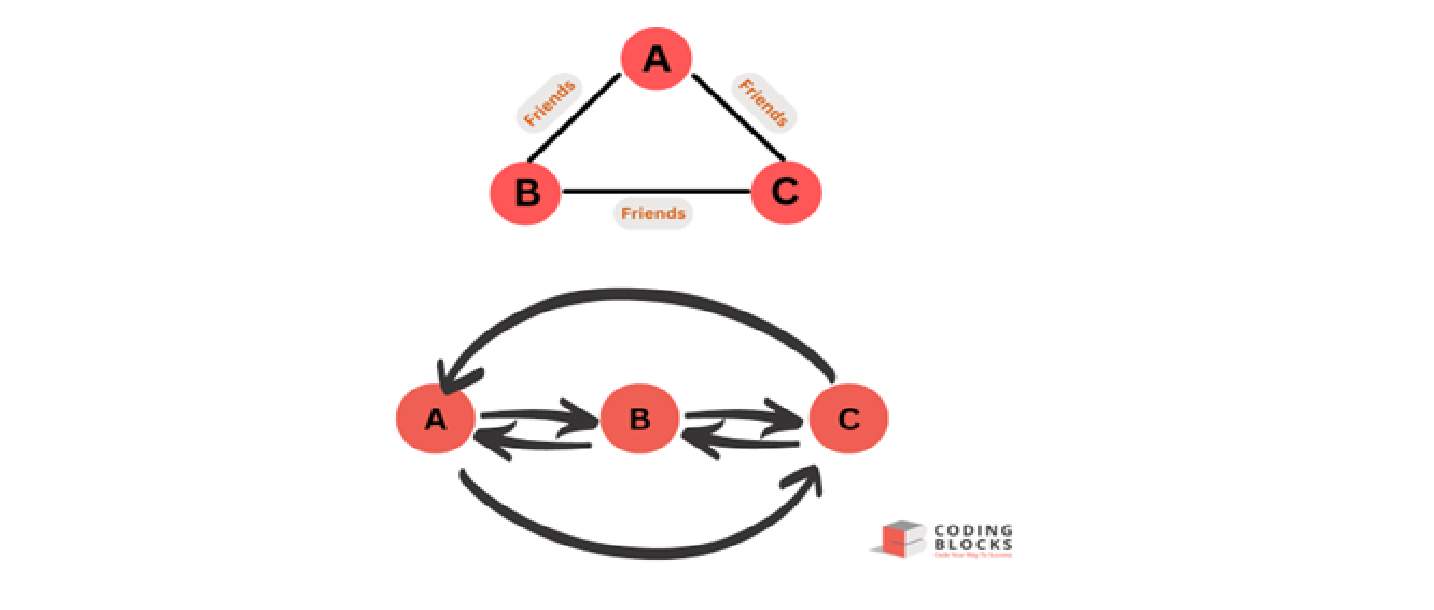
For Example, the below picture signifies that person A follows person B, but B does not follow back A, person B follows person C, but C does not follow back B and similarly person C follows person A, but A does not follow back C.

Undirected Graph:
- An undirected graph is a type of graph structure where the edges have no direction and connect nodes bidirectionally.
- In an undirected graph, there is no distinction between the source and target of an edge, and the edges are represented simply as unordered pairs of vertices.
- Undirected Graph are also used to model relationships in social networking site such as Facebook but in that if you send a friend request to a person and if he/she accepts it then you both become friends. It is a mutual connection and you both can see each other’s posts.
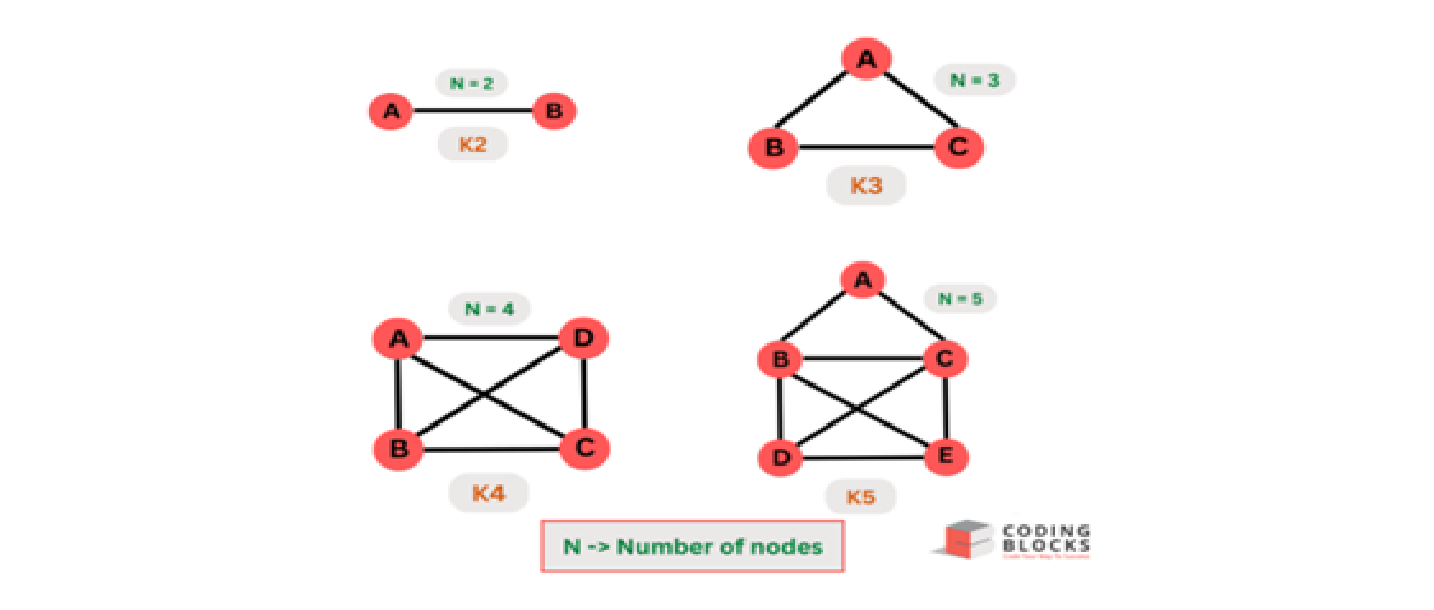
Complete Graph:
- A complete graph is a type of undirected graph where every node is connected to every other node by a unique edge.
- In other words, for a complete graph with n nodes, there are [n(n-1)/2] edges.
- It is denoted by Kn. (where n-> number of nodes/vertices)
Library
WEB DEVELOPMENT
FAANG QUESTIONS

